Belly fat isn’t just about how your clothes fit — it can affect your confidence, energy levels, and even your long-term health. Carrying extra weight around your midsection has been linked to higher risks of heart disease, diabetes, and other metabolic issues.
But here’s the good news: losing belly fat doesn’t mean starving yourself, following extreme trends, or spending hours on endless ab workouts. The key lies in adopting eating strategies that are sustainable, effective, and tailored to your lifestyle.

In this complete guide, we’ll break down the most effective diets for targeting stubborn belly fat. You’ll discover approaches backed by science, from high-protein and low-carb diets to intermittent fasting, Mediterranean-style eating, and smart calorie strategies that actually work in real life.
We’ll also cover tips to curb cravings, manage portion sizes, and balance your meals so you can see results without feeling deprived. By the end of this guide, you’ll have a clear roadmap to eat smarter, reduce belly fat, boost your energy, and feel healthier — all while enjoying food and life, instead of dreading every meal.
FYI: This post may contain affiliate links, which means we may earn a small commission if you make a purchase — at no extra cost to you. We only recommend nutrition plans, meal tools, and healthy products that align with real, science-backed strategies for reducing belly fat naturally.
Top Diets for Losing Belly Fat
1. Ketogenic Diet (Keto Diet)
The Ketogenic Diet, commonly referred to as the Keto Diet, has grown in popularity over the past decade as one of the most effective approaches for weight loss, improved mental clarity, and enhanced metabolic health.
Unlike traditional diets that focus primarily on restricting calories or cutting fat, the keto diet emphasizes macronutrient composition, drastically reducing carbohydrate intake while increasing fat consumption.
This approach shifts the body into a metabolic state known as ketosis, where fat becomes the primary source of energy instead of glucose.

What Is the Keto Diet?
The keto diet is fundamentally a high-fat, moderate-protein, and very low-carbohydrate eating plan.
By limiting carbohydrates to roughly 20–50 grams per day, the body exhausts its glucose reserves and begins breaking down fats into molecules called ketone bodies, which are then used as fuel for the brain and body.
This is a key difference from most standard diets, which rely heavily on glucose as the main energy source.
Key Principles of the Keto Diet
- High Fat Intake: Approximately 70–75% of daily calories come from healthy fats. Sources include avocados, nuts, seeds, olive oil, fatty fish, and grass-fed butter. Fat is the primary energy source, keeping you full and satisfied.
- Moderate Protein: Protein accounts for 20–25% of daily calories, enough to preserve lean muscle mass without interfering with ketosis.
- Low Carbohydrates: Only 5–10% of daily calories come from carbs, focusing on non-starchy vegetables, leafy greens, and low-carb berries. High-carb foods such as bread, pasta, rice, and sugary snacks are avoided.
Why People Follow the Keto Diet
The keto diet has a range of benefits, which is why it appeals to different groups of people:
- Weight Loss: By switching the body’s primary fuel source from carbs to fat, many people experience rapid fat loss, especially around the abdomen and waistline.
- Appetite Control: High-fat and moderate-protein meals help increase satiety, reducing cravings and making it easier to naturally consume fewer calories.
- Stable Energy Levels: With reduced carbohydrate intake, blood sugar spikes are minimized, providing more consistent energy throughout the day.
- Mental Clarity and Focus: Ketones are an efficient fuel for the brain, leading to improved concentration, mental clarity, and cognitive performance.
- Potential Health Benefits: Studies suggest the keto diet may improve blood sugar regulation, insulin sensitivity, and certain heart health markers. Some research also shows potential benefits for neurological conditions, although long-term effects require more study.
Common Variations of the Keto Diet
- Standard Keto Diet (SKD): The most widely used approach, following the classic macronutrient ratio of high fat, moderate protein, and very low carbs.
- Targeted Keto Diet (TKD): Allows additional carbs around workouts for athletes or those with higher energy needs.
- Cyclical Keto Diet (CKD): Involves periods of higher-carb intake, usually 1–2 days per week, to replenish glycogen stores, beneficial for endurance athletes or heavy lifters.
- High-Protein Keto Diet: Similar to SKD but slightly higher in protein (35% of calories), useful for those aiming to preserve or build muscle mass.
Who Can Benefit from the Keto Diet?
The keto diet can be effective for adults seeking:
- Weight loss and fat reduction
- Improved blood sugar and insulin control
- Enhanced mental focus and sustained energy
- Appetite management and reduced cravings
However, it may not be suitable for everyone. Individuals with liver, kidney, or pancreatic conditions, or those who are pregnant, breastfeeding, or have certain metabolic disorders, should consult a healthcare professional before starting keto.
Additionally, beginners should prepare for the “keto adaptation” period, which can include temporary fatigue, brain fog, or digestive changes as the body transitions to burning fat for fuel.
Keto in Daily Life
Following the keto diet requires planning and awareness. It’s not just about cutting carbs; it’s about making smart choices for fats and proteins while ensuring you’re getting essential micronutrients.
Leafy greens, nuts, seeds, and low-carb vegetables should be staples, while processed foods, sugars, and refined carbs are avoided.
Meal prep, tracking macros, and understanding hidden carbs are crucial for long-term success.
With proper guidance and consistency, the keto diet can lead to sustainable weight management, improved metabolic health, and enhanced energy, making it one of the most widely adopted low-carb diets in the world today.
Struggling with weight loss or post-workout recovery? This Vegan Organic Protein Powder keeps you full longer, burns fat naturally, and supports lean muscle growth. Perfect for anyone serious about results.
Grab yours today and start transforming your body the natural way
2. Low-Carb Diet
A Low-Carb Diet is one of the most popular dietary strategies for weight management, metabolic health, and improved energy levels.
Unlike conventional diets that focus on calorie restriction alone, low-carb diets emphasize reducing carbohydrate intake while increasing the consumption of protein and healthy fats.
By limiting carbs, the body becomes more efficient at burning stored fat for energy, leading to weight loss, better blood sugar control, and reduced cravings.
What Is a Low-Carb Diet?
A low-carb diet restricts carbohydrate intake to a level below what most people typically consume.
While the exact number of carbs allowed varies depending on the approach, most low-carb plans aim for 50–150 grams of net carbs per day, coming mainly from vegetables, nuts, seeds, and low-sugar fruits.
Foods high in refined sugars, bread, pasta, rice, and starchy vegetables are minimized or eliminated.
Key Principles of a Low-Carb Diet
- Moderate Protein: Protein intake is emphasized to help maintain lean muscle mass and increase satiety. Sources include lean meats, eggs, fish, and dairy.
- Healthy Fats: Fats provide energy and promote fullness. Avocados, olive oil, nuts, seeds, and fatty fish are common staples.
- Carbohydrate Restriction: Focus is placed on low-glycemic carbs from leafy greens, cruciferous vegetables, berries, and legumes in moderation.
- Balanced Nutrition: While carbs are limited, micronutrient intake is maintained through vegetables, fruits, nuts, and seeds, ensuring essential vitamins and minerals are met.
Why People Follow Low-Carb Diets
- Weight Loss and Fat Reduction: By reducing carb intake, insulin levels decrease, allowing the body to burn stored fat more effectively.
- Improved Blood Sugar Control: Low-carb diets help regulate blood sugar and insulin levels, beneficial for those with insulin resistance or type 2 diabetes.
- Reduced Cravings and Appetite: Protein and fat promote satiety, reducing the likelihood of overeating and snacking on sugary foods.
- Enhanced Energy Levels: Many people report steady energy throughout the day due to fewer blood sugar spikes and crashes.
- Potential Heart Health Benefits: Low-carb diets have been linked to improved triglyceride levels, HDL cholesterol, and blood pressure, although long-term studies are ongoing.
Common Variations of Low-Carb Diets
- Moderate Low-Carb Diet: 100–150 grams of carbs per day; often easier for beginners or those seeking sustainable weight management.
- Strict Low-Carb Diet: 50–100 grams of carbs per day; used for faster fat loss or improved metabolic effects.
- Very Low-Carb/Keto-Style Diet: Less than 50 grams of carbs per day, which may induce ketosis, a metabolic state similar to the ketogenic diet.
Who Should Consider a Low-Carb Diet?
A low-carb diet can benefit adults aiming to:
- Lose excess weight and reduce body fat
- Improve blood sugar control and insulin sensitivity
- Reduce hunger and overeating
- Improve metabolic markers like cholesterol and triglycerides
However, it may not be suitable for individuals with certain liver or kidney conditions, pregnant or breastfeeding women, or anyone with specific dietary restrictions. Consulting a healthcare professional before starting a low-carb diet is recommended.
Low-Carb Diet in Daily Life
Success on a low-carb diet comes from smart food choices and planning. Staples often include:
- Lean proteins: chicken, turkey, fish, eggs
- Healthy fats: avocado, olive oil, coconut oil, nuts
- Low-carb vegetables: spinach, kale, broccoli, cauliflower
- Limited fruits: berries, green apples
- Minimal processed foods and sugars
Meal prepping, reading food labels, and tracking net carb intake can make low-carb dieting manageable and sustainable.
Many people find that after an initial adaptation period, their energy levels, focus, and satiety improve significantly, making it easier to maintain long-term results.
Garden of Life Meal Replacement Shakes, Vegan Raw Organic Protein Powder, Chocolate Protein Powder with Plant Based Pea Protein, Sprouts, Greens, Probiotics, Dairy Free 28 Servings
No more skipping meals or grabbing unhealthy snacks — fuel your body with clean, plant-based nutrition in minutes! With Garden of Life Meal Replacement Shake, you get protein, probiotics, and vitamins in one delicious scoop.
Order now and stay healthy on even your busiest days
3. High-Protein Diet
A High-Protein Diet is widely recognized as one of the most effective approaches for weight management, muscle building, and overall health.
Unlike diets that focus solely on calorie restriction or macronutrient imbalance, a high-protein diet emphasizes increasing protein intake while balancing fats and carbohydrates, helping the body maintain muscle, regulate appetite, and support metabolism.
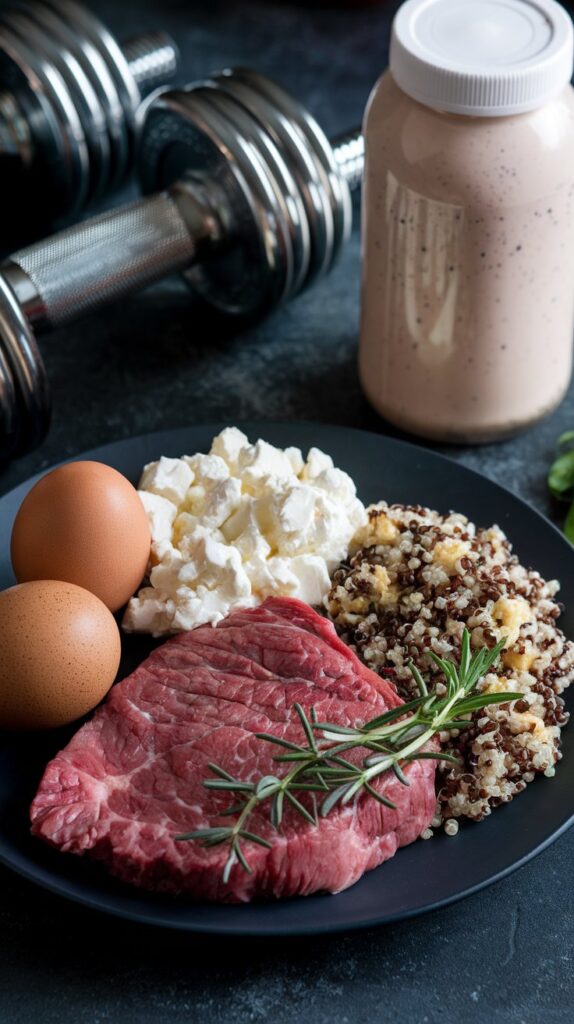

What Is a High-Protein Diet?
A high-protein diet prioritizes protein as the primary macronutrient, typically providing 25–35% of daily calories from protein sources.
Depending on activity level, goals, and body weight, protein intake often ranges from 1.2–2.5 grams per kilogram of body weight.
Proteins are made up of amino acids, which are the building blocks for muscle tissue, hormones, enzymes, and other vital body functions.
Key Principles of a High-Protein Diet
- Prioritize Protein at Every Meal: Include lean meats, eggs, dairy, fish, tofu, or legumes at breakfast, lunch, and dinner.
- Balance Carbs and Fats: Healthy fats and fiber-rich carbohydrates support sustained energy and digestive health.
- Spread Protein Intake Throughout the Day: Eating protein at regular intervals maximizes muscle protein synthesis and keeps hunger in check.
- Include a Variety of Protein Sources: Combining animal and plant-based proteins ensures all essential amino acids are consumed.
Why People Follow a High-Protein Diet
- Muscle Growth and Maintenance: Adequate protein is essential for building and preserving lean muscle, especially during resistance training or weight loss.
- Weight Management: High-protein meals increase satiety, reducing cravings and overall calorie intake, which can promote fat loss.
- Boosted Metabolism: Digesting protein requires more energy than fats or carbs, slightly increasing calorie expenditure through the thermic effect of food.
- Better Blood Sugar Control: Protein slows the absorption of sugar into the bloodstream, helping maintain steady energy levels.
- Supports Recovery: Protein helps repair tissues, recover from workouts, and maintain healthy hair, skin, and nails.
Common Sources of Protein
- Animal-Based: Chicken, turkey, beef, pork, fish, eggs, Greek yogurt, cottage cheese
- Plant-Based: Lentils, chickpeas, quinoa, tofu, tempeh, edamame, nuts, seeds
- Supplements: Whey, casein, pea, and other plant-based protein powders for convenience
Who Can Benefit from a High-Protein Diet?
A high-protein diet is ideal for:
- Individuals seeking weight loss or fat reduction
- Athletes or fitness enthusiasts looking to build muscle and strength
- Older adults aiming to maintain lean mass and prevent sarcopenia
- People wanting to manage hunger and maintain stable energy levels
However, individuals with kidney disease or certain metabolic disorders should consult a healthcare professional before increasing protein intake. For most healthy adults, high-protein diets are safe, effective, and sustainable when balanced with other nutrients.
High-Protein Diet in Daily Life
Practical implementation involves planning meals that prioritize protein without neglecting fiber, vitamins, and healthy fats. Examples include:
- Breakfast: Greek yogurt with berries and chia seeds or scrambled eggs with spinach
- Lunch: Grilled chicken salad with avocado and olive oil
- Dinner: Baked salmon with roasted vegetables and quinoa
- Snacks: Nuts, boiled eggs, or protein shakes
With consistent protein intake, paired with resistance training or physical activity, the body becomes more efficient at building and maintaining muscle, burning fat, and managing hunger.
4. Mediterranean Diet
The Mediterranean Diet is widely celebrated as one of the healthiest eating patterns in the world.
Rooted in the traditional cuisines of countries bordering the Mediterranean Sea, it emphasizes whole, minimally processed foods, healthy fats, lean proteins, and an abundance of fruits and vegetables.
Unlike fad diets that focus on strict restrictions, the Mediterranean diet is flexible, sustainable, and enjoyable, making it easier for people to follow long-term while reaping significant health benefits.
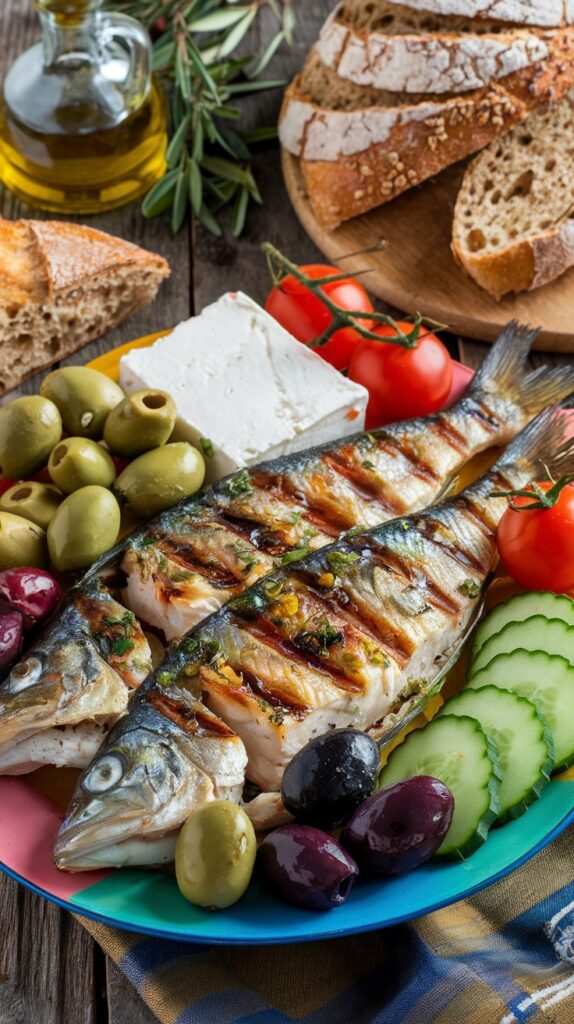

What Is the Mediterranean Diet?
The Mediterranean diet is not a rigid meal plan, but rather a lifestyle approach to eating. Its core principles include:
- High intake of fruits and vegetables: Fresh, seasonal produce provides fiber, vitamins, and antioxidants.
- Healthy fats: Olive oil is the primary fat source, with nuts, seeds, and fatty fish adding omega-3s.
- Lean proteins: Emphasis on fish and seafood, moderate poultry, and limited red meat. Legumes, beans, and eggs provide plant and animal-based proteins.
- Whole grains: Foods like brown rice, quinoa, and whole-grain bread replace refined carbs.
- Herbs and spices: Flavor is enhanced naturally, reducing the need for excessive salt or processed sauces.
- Moderate dairy: Cheese and yogurt are consumed in moderation, often as part of meals or snacks.
- Optional wine consumption: Typically red wine, consumed in moderation and with meals.
Why People Follow the Mediterranean Diet
- Heart Health: Rich in omega-3 fatty acids, monounsaturated fats, and antioxidants, this diet is strongly linked to lower risks of heart disease and stroke.
- Weight Management: By emphasizing whole foods and healthy fats, the diet helps control appetite and promote sustainable weight loss without extreme restrictions.
- Improved Blood Sugar Control: High fiber intake from vegetables, legumes, and whole grains helps stabilize blood sugar and insulin levels, reducing the risk of type 2 diabetes.
- Brain Health: Omega-3s, antioxidants, and polyphenols support cognitive function and may reduce the risk of neurodegenerative diseases.
- Longevity: Studies show populations following Mediterranean-style diets tend to live longer and healthier lives.
Common Foods in the Mediterranean Diet
- Vegetables: Spinach, kale, tomatoes, peppers, cucumbers, eggplants, zucchini
- Fruits: Berries, citrus fruits, grapes, figs, melons
- Healthy Fats: Olive oil, avocado, nuts, seeds, olives
- Proteins: Salmon, sardines, tuna, chicken, beans, lentils, eggs
- Whole Grains: Brown rice, quinoa, whole-grain pasta, oats
- Dairy: Greek yogurt, feta, pecorino, moderate cheese portions
- Herbs & Spices: Basil, oregano, rosemary, garlic, turmeric, cinnamon
Who Can Benefit from the Mediterranean Diet?
The Mediterranean diet is suitable for nearly everyone, especially those looking to:
- Improve heart and metabolic health
- Manage or lose weight without strict dieting
- Support brain health and longevity
- Adopt a sustainable, flexible lifestyle rather than a restrictive plan
It’s particularly beneficial for individuals with prediabetes, high cholesterol, or cardiovascular risk factors, though it can be adapted for general health and wellness goals.
Mediterranean Diet in Daily Life
Implementing the Mediterranean diet involves simple, practical changes rather than drastic restrictions:
- Use olive oil as your main cooking fat.
- Fill half your plate with vegetables and fruits at every meal.
- Choose fish or seafood 2–3 times per week.
- Replace refined carbs with whole grains.
- Snack on nuts, seeds, or fresh fruit instead of processed snacks.
- Limit red meat and sweets to occasional treats, not daily staples.
By focusing on whole foods, balanced macronutrients, and healthy fats, the Mediterranean diet promotes long-term health, satiety, and enjoyment, making it one of the most widely recommended dietary patterns by nutrition experts worldwide.
5. Intermittent Fasting (IF)
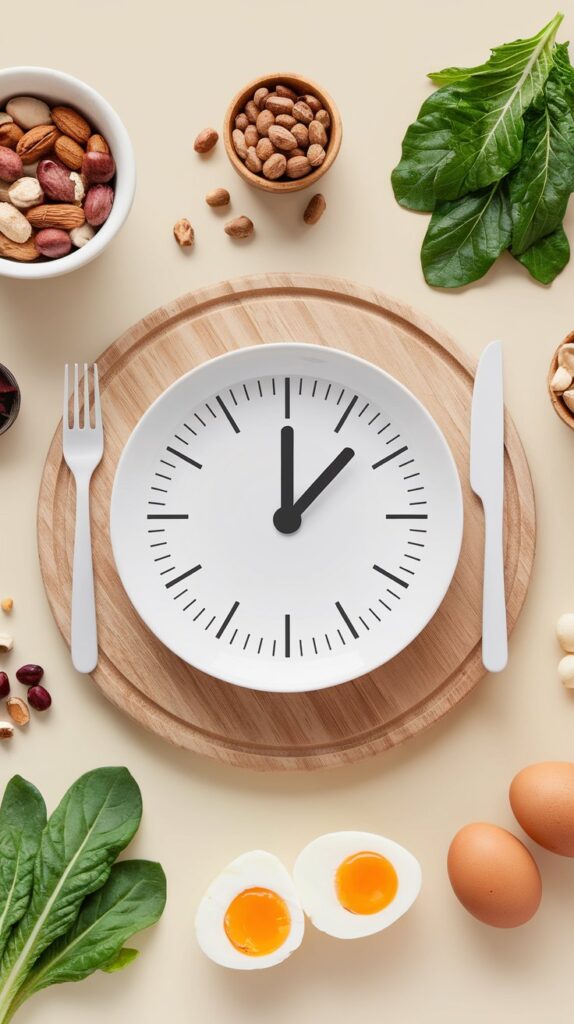

Intermittent Fasting (IF) is a dietary approach that focuses on when you eat rather than what you eat.
Over the past decade, it has gained immense popularity for its potential benefits in weight loss, metabolic health, longevity, and overall well-being. Unlike traditional diets that emphasize calorie restriction every day,
IF involves cycling between periods of eating and fasting, allowing the body to tap into stored fat for energy and improve cellular repair processes.
What Is Intermittent Fasting?
Intermittent fasting is not a diet in the conventional sense—it doesn’t dictate specific foods but rather restricts the eating window. During fasting periods, you abstain from calories but may still consume water, black coffee, or unsweetened tea. Popular IF methods include:
- 16:8 Fasting: Fast for 16 hours and eat during an 8-hour window, often skipping breakfast or late-night snacks.
- 5:2 Method: Eat normally for 5 days and restrict calories to around 500–600 on 2 non-consecutive days.
- Alternate-Day Fasting: Alternate between a day of eating normally and a day of very low-calorie intake.
- One Meal a Day (OMAD): Eat all daily calories in a single meal, fasting for the rest of the day.
How Intermittent Fasting Works
During fasting periods, the body undergoes several metabolic changes:
- Insulin Levels Drop: Lower insulin levels facilitate fat burning and improve insulin sensitivity.
- Increased Human Growth Hormone (HGH): Fasting can increase HGH levels, which aid in muscle preservation and fat loss.
- Cellular Repair: Fasting triggers autophagy, a process where cells remove damaged components and regenerate.
- Calorie Control: Restricting the eating window naturally reduces calorie intake for many people, supporting weight loss.
Why People Follow Intermittent Fasting
- Weight Loss and Fat Reduction: IF promotes fat burning, particularly around the abdomen, while preserving lean muscle mass.
- Improved Metabolic Health: Regular fasting can improve blood sugar control, insulin sensitivity, and cholesterol levels.
- Simplified Eating Patterns: Fewer meals can reduce stress about planning and cooking, making dietary adherence easier.
- Mental Clarity and Focus: Many practitioners report improved concentration and focus during fasting periods due to stable blood sugar levels.
- Potential Longevity Benefits: Studies in animals and humans suggest that intermittent fasting may improve cellular health, reduce inflammation, and promote lifespan extension.
Who Can Benefit from Intermittent Fasting
Intermittent fasting is suitable for many healthy adults, especially those looking to:
- Lose weight or reduce body fat
- Improve metabolic markers such as blood sugar, cholesterol, and triglycerides
- Enhance focus and mental clarity
- Simplify daily eating routines
However, IF may not be suitable for everyone. Pregnant or breastfeeding women, individuals with certain metabolic conditions, or those with a history of eating disorders should consult a healthcare professional before starting.
Intermittent Fasting in Daily Life
Implementing IF is flexible and can be adapted to your lifestyle:
- Start gradually by extending your overnight fast by 1–2 hours.
- Choose an eating window that aligns with your schedule, such as 12–8 PM or 10 AM–6 PM.
- Focus on whole, nutrient-dense foods during eating periods to maximize benefits.
- Stay hydrated and consider electrolytes if fasting for longer periods.
With consistency and proper nutrition, intermittent fasting can be a powerful tool for weight management, metabolic health, and long-term wellness, offering both flexibility and structure in a sustainable way.
INTERMITTENT FASTING COOKBOOK

Best Foods for Burning Belly Fat
Targeting belly fat requires a combination of healthy eating, regular exercise, and lifestyle adjustments.
While no single food can magically melt fat from your midsection, certain foods can boost metabolism, control appetite, and reduce fat storage, making it easier to lose stubborn belly fat.
Incorporating these foods into a balanced diet can accelerate fat loss and support overall health.
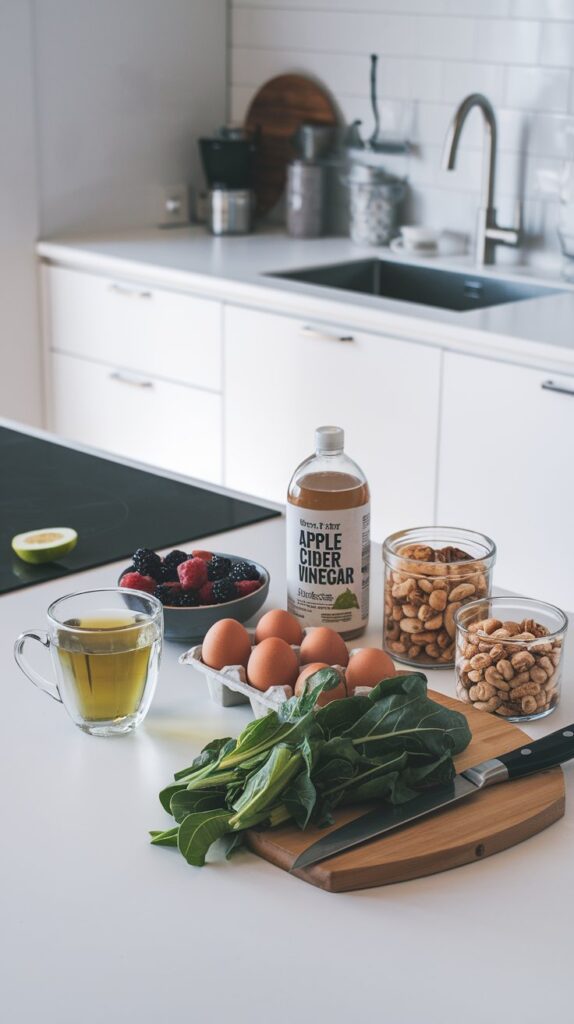

1. Leafy Greens
Leafy greens like spinach, kale, swiss chard, and arugula are low in calories and high in fiber, which helps keep you full and reduces overall calorie intake.
Fiber slows digestion, regulates blood sugar, and can reduce visceral fat—the fat that accumulates around internal organs.
Additionally, leafy greens are packed with vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that support metabolic health and reduce inflammation.
2. Lean Proteins
Protein is critical for fat loss because it boosts metabolism, preserves muscle mass, and increases satiety. Sources include chicken breast, turkey, fish, eggs,
Greek yogurt, and plant-based proteins like lentils and tofu. Eating protein-rich meals can help prevent overeating and stabilize blood sugar, both of which are essential for reducing belly fat.
3. Fatty Fish
Fatty fish such as salmon, mackerel, sardines, and tuna are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which help reduce inflammation and improve insulin sensitivity.
Omega-3s may also promote fat oxidation, making it easier for the body to burn stored fat, especially around the abdominal area. Including fatty fish in your meals 2–3 times per week is highly beneficial for both fat loss and heart health.
4. Whole Grains
Whole grains like oats, quinoa, brown rice, and barley are high in fiber and complex carbohydrates, which stabilize blood sugar levels and promote long-lasting energy. Unlike refined grains,
whole grains prevent sharp insulin spikes, which can contribute to belly fat accumulation. Choosing whole grains over white bread or pasta can make a significant difference in your fat loss efforts.
5. Berries
Berries such as blueberries, raspberries, strawberries, and blackberries are low in calories and high in antioxidants, fiber, and vitamins.
Fiber slows digestion, helps control appetite, and reduces visceral fat. Anthocyanins, the antioxidants that give berries their vibrant color, may also promote fat oxidation and support metabolic health.
6. Nuts and Seeds
Almonds, walnuts, chia seeds, and flaxseeds are rich in healthy fats, protein, and fiber, which help increase satiety and prevent overeating.
Nuts and seeds also provide magnesium and other micronutrients that support metabolism and fat loss. Moderation is key—stick to small portions (a handful or 1–2 tablespoons) to avoid excess calories.
7. Avocados
Avocados are a nutrient-dense fruit packed with monounsaturated fats, fiber, and potassium. Healthy fats help regulate hormones that control appetite and fat storage, while fiber slows digestion and keeps you full. Avocados can be added to salads, smoothies, or eaten as a snack to support belly fat reduction.
8. Green Tea
Green tea is rich in catechins, antioxidants that may boost metabolism and enhance fat burning.
Regular consumption of green tea has been associated with reductions in abdominal fat and overall body weight.
Drinking 2–3 cups daily, particularly before workouts, can complement a fat-loss plan.
9. Greek Yogurt
Greek yogurt is high in protein and probiotics, which support muscle preservation and gut health.
A healthy gut microbiome has been linked to reduced abdominal fat, improved digestion, and better metabolism. Opt for unsweetened, full-fat or low-fat Greek yogurt for the best results.
10. Cruciferous Vegetables
Vegetables like broccoli, cauliflower, Brussels sprouts, and cabbage are low in calories but high in fiber and nutrients, which help regulate blood sugar and keep you feeling full.
Cruciferous vegetables also contain compounds that support liver function and fat metabolism, contributing to belly fat reduction.
Tips for Incorporating These Foods
- Aim to fill half your plate with vegetables and leafy greens at each meal.
- Include a source of lean protein at every meal to maintain muscle and promote satiety.
- Snack on nuts, seeds, or Greek yogurt instead of processed foods.
- Replace refined grains with whole grains like oats or brown rice.
- Include fatty fish 2–3 times per week for healthy fats and omega-3s.
- Drink green tea daily for a natural metabolism boost.
Final Thoughts
Reducing belly fat requires consistency, a balanced diet, and active lifestyle choices. Incorporating these fat-burning foods can help control appetite, boost metabolism, and reduce visceral fat, making it easier to achieve a leaner, healthier midsection.
Pairing these foods with strength training, cardio, and proper sleep creates a holistic approach that maximizes results and supports long-term health.
Fuel your body the clean and natural way! The Garden of Life Vegan Raw Organic Protein Powder is packed with 20g+ of plant-based protein, probiotics, and essential nutrients for energy, weight management, and muscle recovery. Perfect for busy mornings or post-workout shakes!
Grab yours today and transform your nutrition with clean plant power
7-Day Belly Fat Loss Meal Plan
Losing belly fat isn’t just about calorie restriction—it’s about eating the right foods at the right times to boost metabolism, control hunger, and reduce visceral fat.
A well-structured 7-day meal plan can help you adopt healthier eating habits, improve digestion, and accelerate fat loss.
This plan emphasizes high-protein, fiber-rich, and nutrient-dense foods while minimizing refined carbs and added sugars.

Day 1 Sample Meal Plan:
Breakfast: Scrambled eggs with avocado and spinach
Lunch: Grilled salmon with quinoa and steamed broccoli
Dinner: Chicken stir-fry with cauliflower rice
Snack: Greek yogurt with nuts and berries
(Repeat similar meals using the diets above for the rest of the week)
Day 1
Breakfast:
- Scrambled eggs with spinach and cherry tomatoes
- 1 slice of whole-grain toast
- Green tea
Snack:
- Handful of almonds
- 1 small apple
Lunch:
- Grilled salmon with steamed broccoli and quinoa
- Mixed green salad with olive oil and lemon
Snack:
- Greek yogurt with blueberries and chia seeds
Dinner:
- Roasted chicken breast with roasted Brussels sprouts and cauliflower rice
- Side of avocado slices
Day 2
Breakfast:
- Overnight oats made with unsweetened almond milk, chia seeds, and raspberries
- Black coffee or green tea
Snack:
- Baby carrots with hummus
Lunch:
- Turkey and avocado lettuce wraps
- Side of roasted zucchini and bell peppers
Snack:
- Handful of walnuts
Dinner:
- Grilled shrimp with sautéed spinach and garlic
- Brown rice or quinoa (small portion)
Day 3
Breakfast:
- Greek yogurt parfait with strawberries, flaxseeds, and unsweetened coconut flakes
- Green tea
Snack:
- Celery sticks with almond butter
Lunch:
- Baked cod with roasted asparagus and cherry tomatoes
- Side salad with olive oil vinaigrette
Snack:
- Hard-boiled eggs
Dinner:
- Grilled chicken thighs with sautéed broccoli and cauliflower mash
- Small portion of quinoa
Day 4
Breakfast:
- Spinach and mushroom omelet with 2 eggs
- ½ avocado
- Black coffee
Snack:
- Handful of almonds and blueberries
Lunch:
- Grilled salmon salad with mixed greens, cucumber, and olive oil dressing
- ½ cup cooked brown rice
Snack:
- Greek yogurt with chia seeds
Dinner:
- Lean beef stir-fry with broccoli, bell peppers, and snap peas
- Cauliflower rice
Day 5
Breakfast:
- Protein smoothie: spinach, frozen berries, unsweetened almond milk, protein powder, chia seeds
- Green tea
Snack:
- Carrot sticks and hummus
Lunch:
- Grilled chicken with roasted zucchini and asparagus
- Side salad with olive oil and lemon
Snack:
- Handful of walnuts
Dinner:
- Baked cod with roasted Brussels sprouts and cauliflower mash
- ½ avocado on the side
Day 6
Breakfast:
- Scrambled eggs with kale, cherry tomatoes, and 1 slice whole-grain toast
- Green tea
Snack:
- Greek yogurt with blueberries and flaxseeds
Lunch:
- Turkey lettuce wraps with avocado, cucumber, and tomato
- Steamed broccoli on the side
Snack:
- Handful of almonds
Dinner:
- Grilled salmon with roasted cauliflower and asparagus
- Small portion of quinoa
Day 7
Breakfast:
- Omelet with mushrooms, spinach, and feta cheese
- ½ avocado
- Black coffee
Snack:
- Celery sticks with almond butter
Lunch:
- Grilled chicken salad with olive oil and lemon
- Steamed broccoli and roasted bell peppers
Snack:
- Greek yogurt with chia seeds and raspberries
Dinner:
- Baked cod or salmon with roasted Brussels sprouts and cauliflower rice
- Small side salad with leafy greens

Tips for Maximizing Belly Fat Loss
Losing belly fat requires more than just cutting calories—it’s about combining proper nutrition, exercise, and lifestyle habits to target visceral fat and support overall health. Here’s a comprehensive guide to help you accelerate belly fat loss safely and effectively.
1. Prioritize Protein in Every Meal
Protein plays a key role in fat loss, muscle preservation, and satiety. Eating adequate protein helps maintain lean muscle while your body burns fat for energy, particularly around the midsection. Include sources like:
- Lean meats: chicken, turkey, lean beef
- Fish: salmon, tuna, mackerel
- Eggs and Greek yogurt
- Plant-based proteins: lentils, chickpeas, tofu, quinoa
2. Focus on Fiber-Rich Foods
High-fiber foods slow digestion, reduce hunger, and help stabilize blood sugar levels. Soluble fiber, in particular, can help reduce visceral fat—the fat stored around your organs. Incorporate:
- Leafy greens: spinach, kale, arugula
- Cruciferous vegetables: broccoli, cauliflower, Brussels sprouts
- Fruits: berries, apples, pears
- Whole grains: oats, quinoa, brown rice
- Legumes: lentils, chickpeas, black beans
3. Include Healthy Fats
Contrary to outdated dieting advice, healthy fats support hormone regulation, satiety, and fat metabolism. Opt for unsaturated fats like:
- Avocados
- Nuts and seeds
- Olive oil
- Fatty fish rich in omega-3s: salmon, mackerel, sardines
Avoid trans fats and highly processed oils, as these can contribute to belly fat accumulation.
4. Reduce Added Sugar and Refined Carbs
Excess sugar and refined carbs trigger insulin spikes, promoting fat storage, especially around the abdomen. Minimize:
- Sugary drinks: soda, energy drinks, sweetened coffee
- White bread, pasta, and rice
- Pastries, cookies, and candies
Instead, focus on whole grains, vegetables, and naturally sweet fruits for steady energy and fat-burning support.
5. Incorporate Strength Training and Cardio
Exercise is essential for burning calories, boosting metabolism, and building lean muscle. A balanced workout plan includes:
- Strength training: squats, lunges, push-ups, and resistance exercises target muscles and increase resting calorie burn.
- Cardio: brisk walking, running, cycling, or HIIT can accelerate fat loss.
- Core workouts: planks, leg raises, and other abdominal exercises help tone muscles but don’t directly burn belly fat—they improve appearance as overall fat decreases.
6. Get Enough Sleep
Lack of sleep increases cortisol, a stress hormone linked to abdominal fat storage. Aim for 7–9 hours of quality sleep per night to support metabolism, reduce cravings, and improve recovery from workouts.
7. Manage Stress
Chronic stress raises cortisol levels, which can increase belly fat accumulation. Reduce stress through:
- Mindfulness and meditation
- Deep breathing exercises
- Light physical activity like walking or yoga
- Maintaining social connections and hobbies
8. Stay Hydrated
Drinking enough water supports digestion, metabolism, and satiety, making it easier to lose belly fat. Aim for 2–3 liters per day, and consider drinking water before meals to prevent overeating.
9. Track Your Eating Habits
Keeping a food diary or using an app helps you identify patterns, avoid hidden calories, and maintain accountability. Tracking meals, snacks, and drinks ensures your nutrition aligns with your fat-loss goals.
10. Be Consistent and Patient
Belly fat loss doesn’t happen overnight. Combine nutrition, exercise, and lifestyle changes consistently for several weeks to see visible results. Focus on progress, not perfection, and celebrate small milestones along the way.
Final Thoughts
Maximizing belly fat loss requires a holistic approach—nutrition, exercise, sleep, stress management, and consistency all work together.
By prioritizing protein, fiber, and healthy fats, avoiding sugar and refined carbs, and following an active lifestyle, you can accelerate fat loss, improve metabolic health, and achieve a leaner midsection sustainably.
Additional Tips to Boost Results
While a balanced diet and regular exercise are the foundation for losing belly fat, there are several additional strategies that can accelerate results.
These tips focus on optimizing metabolism, reducing fat storage, and making the fat-loss journey more effective and sustainable.
1. Practice Intermittent Fasting
Intermittent fasting (IF) involves cycling between periods of eating and fasting. Popular methods like 16:8 fasting (16 hours fasting, 8 hours eating) can help:
- Reduce overall calorie intake without feeling deprived
- Improve insulin sensitivity and blood sugar regulation
- Promote fat burning, especially in the abdominal area
Combining IF with a balanced, nutrient-dense diet can make belly fat loss faster and more manageable.
2. Drink Green Tea or Coffee
Both green tea and black coffee can slightly boost metabolism due to their caffeine content and bioactive compounds:
- Green tea: Rich in catechins, which may promote fat oxidation
- Coffee: Can temporarily increase calorie burning and improve workout performance
Drinking 1–2 cups of green tea or black coffee before a workout can help enhance fat-burning efficiency.
3. Use Smaller Plates and Mindful Eating
Eating slowly and practicing mindful eating helps you notice hunger and fullness cues, preventing overeating.
Using smaller plates, chewing thoroughly, and avoiding distractions like TV or phones during meals can reduce overall calorie intake and support belly fat reduction.
4. Incorporate High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT)
HIIT alternates between short bursts of intense activity and recovery periods. It is highly effective for:
- Burning calories quickly
- Boosting metabolism after exercise
- Targeting stubborn belly fat through overall fat reduction
Examples include sprint intervals, jump squats, burpees, or cycling sprints for 20–30 minutes.
5. Eat More Fiber, Especially Soluble Fiber
Soluble fiber absorbs water and forms a gel in the gut, slowing digestion and reducing fat storage around the abdomen. Foods high in soluble fiber include:
- Oats
- Lentils and beans
- Apples, pears, and berries
- Flaxseeds and chia seeds
Adding fiber to every meal can increase satiety, control cravings, and support fat loss.
6. Prioritize Strength Training
While cardio burns calories, strength training builds lean muscle, which:
- Increases resting metabolic rate (burns more calories at rest)
- Enhances body composition by reducing fat and toning muscles
- Improves insulin sensitivity
Focus on compound exercises like squats, deadlifts, push-ups, and rows 3–4 times per week for optimal results.
7. Manage Stress and Sleep
High stress and poor sleep can increase cortisol levels, leading to abdominal fat accumulation. Strategies to manage stress include:
- Meditation or deep-breathing exercises
- Yoga or light physical activity
- Prioritizing 7–9 hours of sleep per night
A calm mind and adequate rest support hormonal balance and fat loss.
8. Track Progress, Not Perfection
Measure results using multiple methods:
- Body measurements: Waist, hips, and thighs
- Progress photos: Weekly or biweekly
- Fitness tracking: Strength gains and endurance improvements
Tracking progress helps you stay motivated and adjust your plan if results plateau.
9. Stay Consistent and Patient
Belly fat loss is often the most stubborn area to change, so patience and consistency are crucial. Avoid quick fixes or crash diets. Focus on long-term lifestyle changes that are sustainable, enjoyable, and effective.
Final Thoughts
Losing belly fat is a gradual process that requires a combination of smart nutrition, effective exercise, and sustainable lifestyle habits.
While many people seek quick fixes, the most reliable results come from consistent, long-term strategies rather than fad diets or extreme measures.
Key takeaways include:
- Prioritize whole, nutrient-dense foods: Focus on protein, fiber, healthy fats, and low-glycemic carbohydrates to support fat loss and overall health.
- Incorporate strength training and cardio: Building lean muscle boosts metabolism, while cardio helps burn calories and reduce visceral fat.
- Use additional strategies to boost results: Intermittent fasting, HIIT, mindful eating, and proper hydration can accelerate belly fat loss when combined with a balanced diet.
- Manage stress and sleep: Adequate sleep and stress management regulate hormones like cortisol, which play a major role in fat storage around the midsection.
- Be patient and consistent: Belly fat is often the last area to change, so results may take time. Focus on sustainable habits rather than quick fixes.
Remember, spot reduction is not realistic—fat loss occurs throughout the body.
By following a holistic approach that includes healthy eating, regular exercise, and lifestyle adjustments, you can reduce belly fat, improve metabolic health, and achieve a leaner, stronger, and healthier body.
The journey to a flatter midsection is not just about appearance; it’s about long-term wellness, energy, and confidence. Stay consistent, make mindful choices, and celebrate small victories along the way.
Losing belly fat can be challenging, and many people unknowingly sabotage their efforts with habits or strategies that are ineffective or even counterproductive. Knowing these common mistakes can help you stay on track, maximize results, and avoid frustration.
1. Relying Solely on Crunches or Ab Exercises
Many believe that doing endless sit-ups or ab workouts will melt belly fat. While core exercises strengthen and tone muscles, they cannot specifically burn fat in the midsection.
Belly fat is primarily reduced through overall fat loss via a combination of diet, cardio, and strength training.
2. Skipping Meals or Severely Restricting Calories
Severely cutting calories might seem like a shortcut, but it often slows metabolism, reduces energy, and increases cravings.
This can lead to overeating later or loss of muscle mass. Focus on moderate calorie control combined with nutrient-dense foods rather than extreme fasting unless carefully planned.
3. Consuming Hidden Sugars and Refined Carbs
Sugary drinks, sweets, and refined carbs cause insulin spikes, which encourage fat storage, particularly around the belly.
Even foods labeled “healthy” can contain hidden sugar, such as flavored yogurts, granola bars, or packaged snacks. Reading labels and prioritizing whole foods is key.
4. Ignoring Strength Training
Relying only on cardio for fat loss can result in muscle loss, which slows metabolism and makes long-term fat loss harder.
Incorporating resistance training builds lean muscle, increases resting calorie burn, and enhances body composition.
5. Expecting Immediate Results
Belly fat is often the most stubborn type of fat, especially around the organs. Expecting quick results can lead to disappointment.
Sustainable fat loss requires consistency, patience, and long-term lifestyle changes.
6. Neglecting Sleep and Stress Management
Poor sleep and chronic stress increase cortisol, a hormone linked to belly fat storage.
Even with a perfect diet and exercise plan, lack of rest or high stress can slow fat loss. Aim for 7–9 hours of quality sleep and implement stress-reduction techniques like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing.
7. Overestimating Exercise and Underestimating Food Intake
Many people assume that burning calories in the gym cancels out poor eating choices, but diet plays the larger role in fat loss.
Overeating even “healthy” foods can stall progress. Track portions and maintain a balanced, nutrient-dense diet to complement your workouts.
8. Falling for Quick-Fix Solutions
Supplements, waist trainers, detox teas, or fad diets often promise rapid belly fat loss but lack scientific support.
Sustainable results come from realistic lifestyle changes, not gimmicks. Focus on whole foods, consistent exercise, and healthy habits.
Final Thoughts
Avoiding these mistakes ensures your belly fat loss journey is efficient, safe, and sustainable.
By combining a balanced diet, proper exercise, stress management, and realistic expectations, you set yourself up for long-term success—achieving a leaner midsection while improving overall health.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About Belly Fat Loss
Losing belly fat is a common goal, but it can be confusing due to conflicting advice and myths. Here’s a detailed FAQ addressing the most common concerns:
1. Can I Lose Belly Fat Without Exercise?
While a healthy diet alone can reduce overall body fat, combining it with exercise speeds up fat loss and improves body composition. Strength training preserves muscle, and cardio helps burn extra calories. For best results, a balanced approach of diet and exercise is recommended.
2. How Long Does It Take to Lose Belly Fat?
The timeline varies depending on starting body fat, diet, exercise, and consistency. On average, with a proper plan, noticeable results can appear in 4–8 weeks, while significant reductions may take 3–6 months. Patience and consistency are key.
3. Is Spot Reduction Possible?
No. You cannot target fat loss in a specific area. Belly fat decreases as you lose overall body fat through calorie deficit, strength training, and cardio. Core exercises help tone abdominal muscles, improving appearance as fat is reduced.
4. What Foods Help Burn Belly Fat?
Foods high in protein, fiber, and healthy fats support fat loss. Examples include:
- Lean proteins: chicken, fish, eggs
- High-fiber vegetables and fruits: leafy greens, berries, broccoli
- Whole grains: oats, quinoa, brown rice
- Healthy fats: avocado, nuts, olive oil
Avoid excessive sugar, refined carbs, and processed foods.
5. Can Intermittent Fasting Help Reduce Belly Fat?
Yes, intermittent fasting (IF) can help by:
- Reducing calorie intake
- Improving insulin sensitivity
- Promoting fat burning during fasting periods
Popular methods like 16:8 fasting can complement a balanced diet and exercise plan for belly fat reduction.
6. How Much Cardio Should I Do to Lose Belly Fat?
A mix of moderate-intensity cardio (like brisk walking or cycling) and high-intensity interval training (HIIT) is ideal. Aim for 150–300 minutes of moderate cardio or 75–150 minutes of vigorous cardio per week, combined with strength training 2–4 times weekly.
7. Does Stress Cause Belly Fat?
Yes. Chronic stress increases cortisol levels, which can promote fat storage, particularly around the abdomen. Managing stress through meditation, yoga, deep breathing, and adequate sleep can support belly fat loss.
8. Are Supplements Effective for Belly Fat Loss?

Most supplements claiming to “burn belly fat” have limited scientific support. While some may offer minor benefits (e.g., green tea extract), the foundation must be a healthy diet, exercise, and lifestyle habits. Supplements should never replace whole foods or sustainable habits.
9. Can Women and Men Lose Belly Fat the Same Way?
Yes and no. Both genders benefit from diet, cardio, and strength training, but hormonal differences can make men lose belly fat slightly faster, while women may store more fat around the hips and lower abdomen. Consistency and lifestyle adjustments remain key for everyone.
10. How Do I Maintain Belly Fat Loss Long-Term?
Maintaining results requires sustainable lifestyle changes:
Avoiding crash diets or extreme restrictions
Consistency is more effective than temporary extreme measures.
Balanced, nutrient-dense diet
Regular exercise with strength and cardio
Adequate sleep and stress management
Conclusion
Reducing belly fat is not about quick fixes or extreme diets—it’s about adopting sustainable, science-backed habits that support fat loss, improve metabolism, and enhance overall health. By focusing on a combination of balanced nutrition, regular exercise, stress management, and proper sleep, you create the optimal environment for your body to burn fat effectively.
Key points to remember:
- Nutrition is foundational: Prioritize protein, fiber, healthy fats, and whole foods while minimizing refined carbs and added sugars.
- Exercise strategically: Combine strength training, cardio, and core workouts to burn calories, preserve muscle, and tone your midsection.
- Lifestyle matters: Stress management, quality sleep, and hydration significantly influence belly fat reduction.
- Patience and consistency are essential: Belly fat is often the last fat to lose, so sustainable habits will yield long-term results.
Ultimately, achieving a leaner midsection is about creating a healthy, maintainable lifestyle rather than seeking rapid, short-lived results.
By implementing the strategies outlined in this guide—eating wisely, moving your body, and supporting recovery—you can lose belly fat, improve overall wellness, and maintain your results for life.




